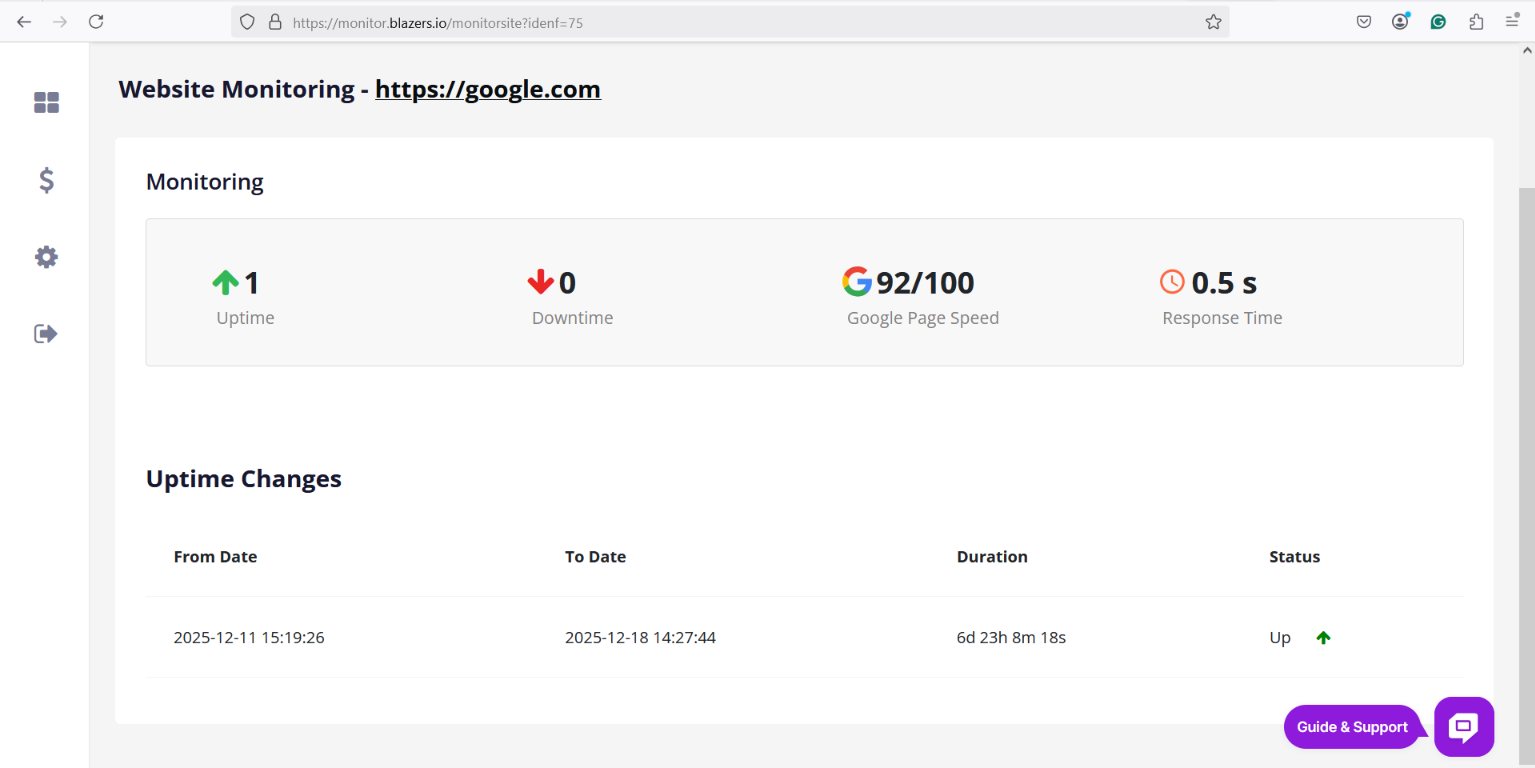
1. Uptime
Uptime refers to how long your website or server stays active and accessible without interruption.
- It is usually measured in percentage (%)
- Example standards: 99%, 99.9%, 99.99% uptime
- Higher uptime = more reliable website
Why it matters:
- If your site is down, users can’t access it
- It affects customer trust, conversions, and SEO ranking
2. Downtime (Monitoring downtime)
Downtime is the opposite of uptime. It is the period when your website is unavailable, fails to load, or responds with errors.
A downtime monitor does:
- Continuously checks your site at regular intervals (Ex: every 1 min, 5 min)
- Detects when your site stops responding
- Sends alerts/notifications (email, SMS, Slack, etc.)
- Helps identify issues early
Causes of downtime:
- Server overload
- Hosting failure
- DNS issues
- Code errors
- Expired SSL certificate
3. Google Page Speed
Google Page Speed usually refers to Google PageSpeed Insights, a tool used to measure your website’s performance.
It analyzes:
- How fast your webpage loads
- Performance on mobile + desktop
- Core Web Vitals (LCP, FID, CLS)
It provides:
- A performance score (0–100)
- Suggestions to improve speed
Good page speed helps:
- Better user experience
- Boost SEO ranking
- Increase conversion rate
4. Response Time
Response time is the time taken by the server to respond to a request.
Example:
- When a user opens your website, the server processes the request and sends data back.
- The amount of time this takes = response time
Usually measured in:
- milliseconds (ms)
- lower time = better performance
Factors affecting response time:
- Server processing power
- Network latency
- Database queries
- Page size and code complexity